Every child deserves the chance to thrive, and for some, that means getting a little extra help with movement and physical development. Physical therapy can support kids in reaching their full potential, whether they’re overcoming physical challenges or simply building stronger skills. In this blog, we’ll explore what Physical Therapy is, how Pediatric Physical Therapy works and how it can make a big difference in your child’s growth, confidence, and overall well-being.
What is Physical Therapy?
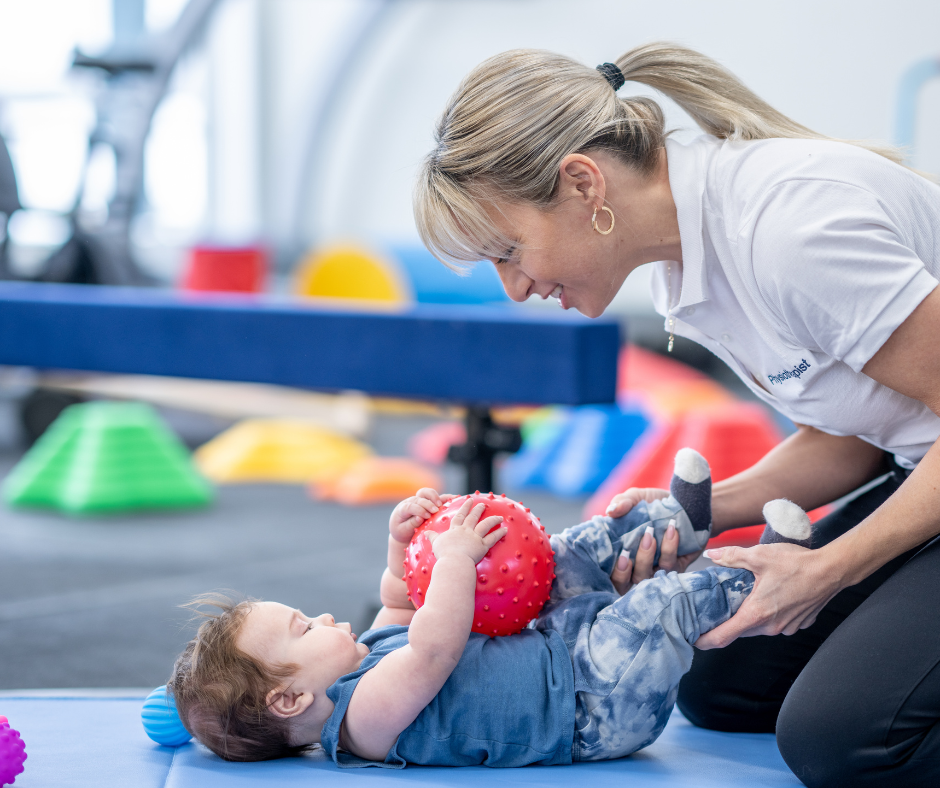

Physical therapy (PT) is all about helping people move better and feel stronger. It uses exercises, hands-on techniques, and different methods to reduce pain, improve mobility, and restore function. Whether your child is recovering from an injury, surgery, or dealing with a condition that affects their muscles or movement, physical therapy can make a big difference in their daily life.
How Does Pediatric Physical Therapy Work?
Pediatric physical therapists follow a clear plan to give children the best possible care. They start with an evaluation, set achievable goals, and develop interventions to meet those goals. Here’s how it breaks down:
Evaluation
This step helps determine what’s causing the problem and how to help the child.

Prognosis
The therapist will set realistic goals to work toward.

Intervention
The action plan—the exercises and activities the child will do to meet their goals.

Outcome Evaluation
Progress is checked regularly to see how well the plan is working and to adjust it if needed.

How is Physical Therapy Different from Occupational Therapy and Speech Therapy?
Physical therapy often works alongside other therapies like occupational therapy (OT) and speech therapy, but each one focuses on different areas of development:
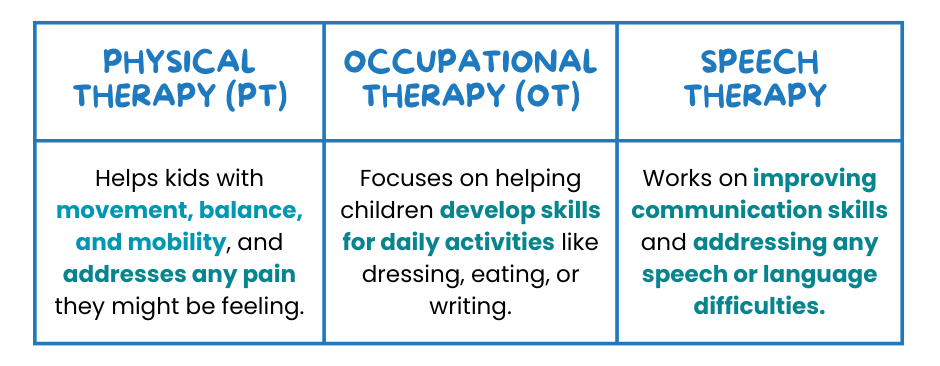
Each therapy serves a unique purpose, and understanding the differences can help ensure your child gets the care they need.
Who Benefits from Pediatric Physical Therapy?
Pediatric physical therapy can help children dealing with a variety of challenges, including:
- Developmental delays
- Autism
- Downs Syndrome
- Muscular dystrophy
- Cerebral palsy
- Recovery from surgery
- Sports-related injuries
Examples of tasks that may be challenging:

Maintaining ring sitting with upright posture during circle time

Transitioning from the floor to standing

Negotiating stairs or curbs

Jumping

Standing on one foot

Throwing/catching a ball
Children who struggle with balance, coordination, or gross motor skills can greatly benefit from physical therapy.
What Does a Pediatric Physical Therapist Do?
- Promote Independence – Pediatric physical therapists help children develop the skills needed to perform daily activities independently.
- Enhance Mobility – They work to improve a child’s movement, balance, and strength to enhance their mobility.
- Improve Motor skills – Therapists assist children in developing gross and fine motor skills essential for tasks like walking and grasping objects.
- Address Developmental Delays – Pediatric physical therapists create individualized plans to help children overcome developmental delays and reach important milestones.
- Correct Movement Patterns – They work on correcting inefficient movement patterns to promote safer and more effective physical activity.
- Posture Control – Improving posture by strengthening core muscles and teaching proper body alignment.
- Rehabilitation after injury or surgery – They guide children through rehabilitation exercises to restore strength and function after injury or surgery.
- Providing education and empowering parents and families – PTs educate and support families with home activities to aid in the child’s progress.
Physical Therapy Techniques for Kids
Therapists use a variety of techniques to engage children and help them meet their goals:
- Therapeutic Exercises
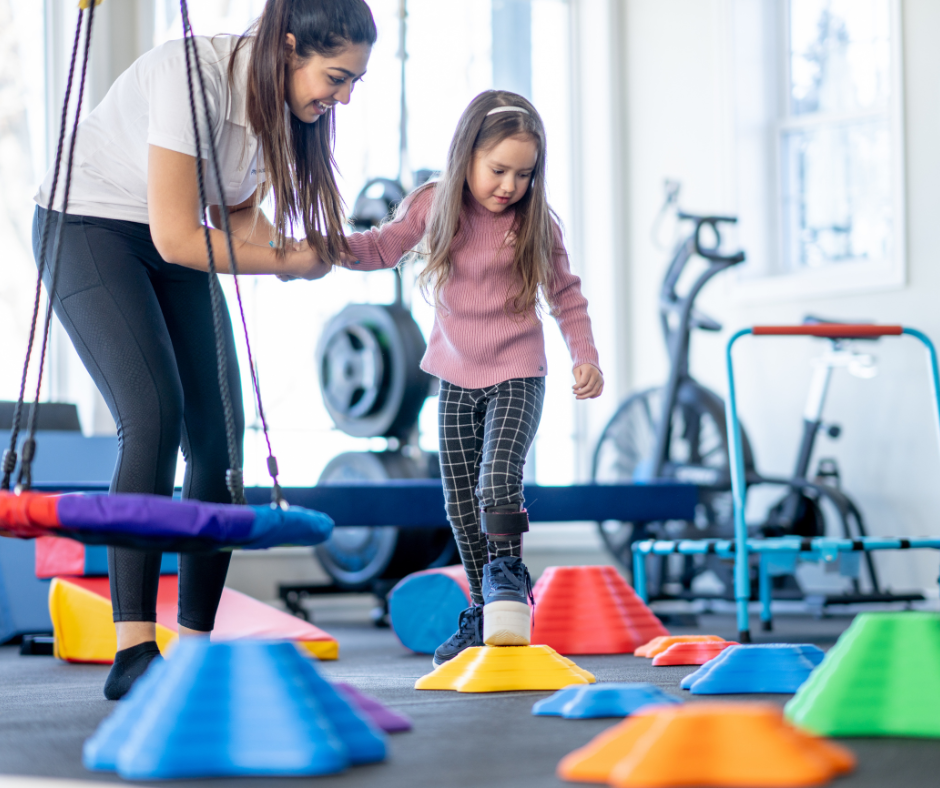

Therapeutic Exercises are fun, engaging activities that build strength, flexibility, and endurance. These exercises are designed to improve strength, flexibility, and endurance, but for kids, they’re modified as fun activities:
- Obstacle Courses: Navigating through tunnels, stepping over obstacles, and crawling under low bridges to improve motor planning and balance.
- Ball Games: Throwing, catching, or kicking a ball to enhance upper and lower body strength.
- Play-Based Therapy
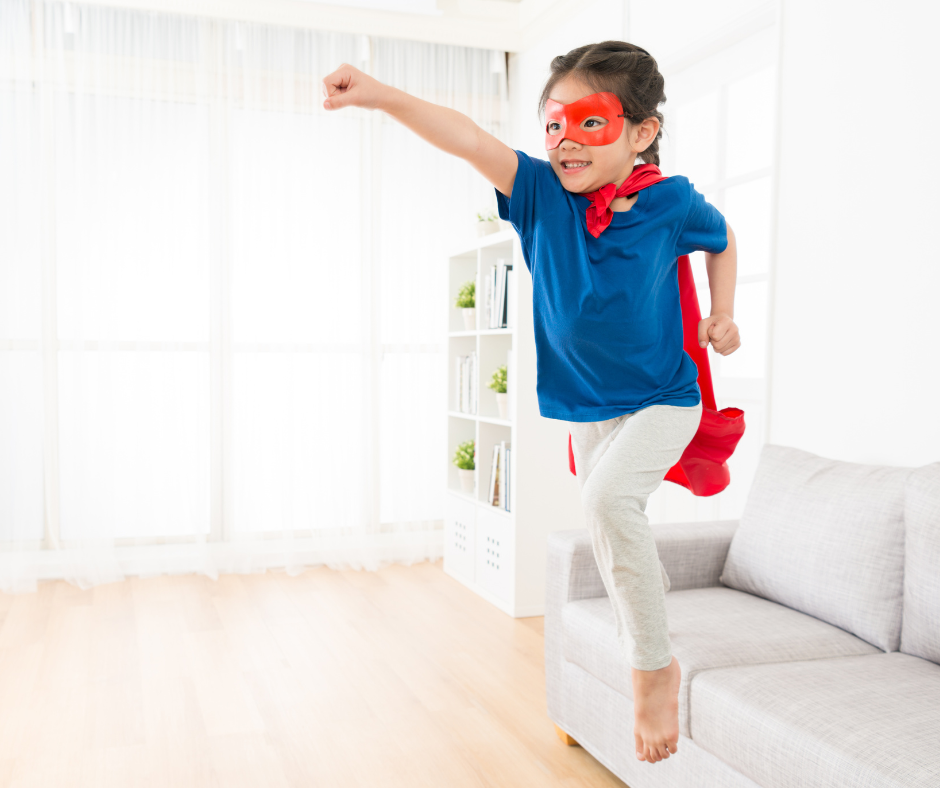

Children learn best through play. Physical therapists often incorporate toys, games, or imaginative scenarios (like pretending to be superheroes or animals) to encourage movement, motor planning, and coordination in an enjoyable way.
- Mobility Training
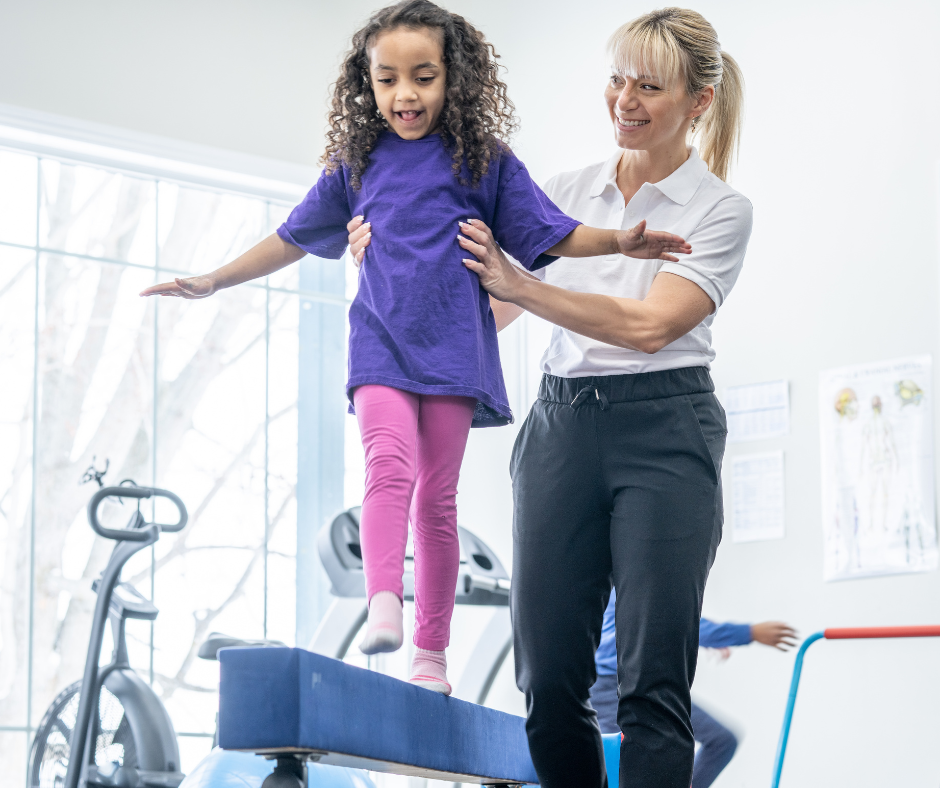

Focusing on balance, coordination, and body awareness, therapists use tasks such as balancing on beams, hopping on one foot, or walking on uneven surfaces to help kids move with more control and confidence. This helps children with everyday activities like walking, running, and climbing stairs.
